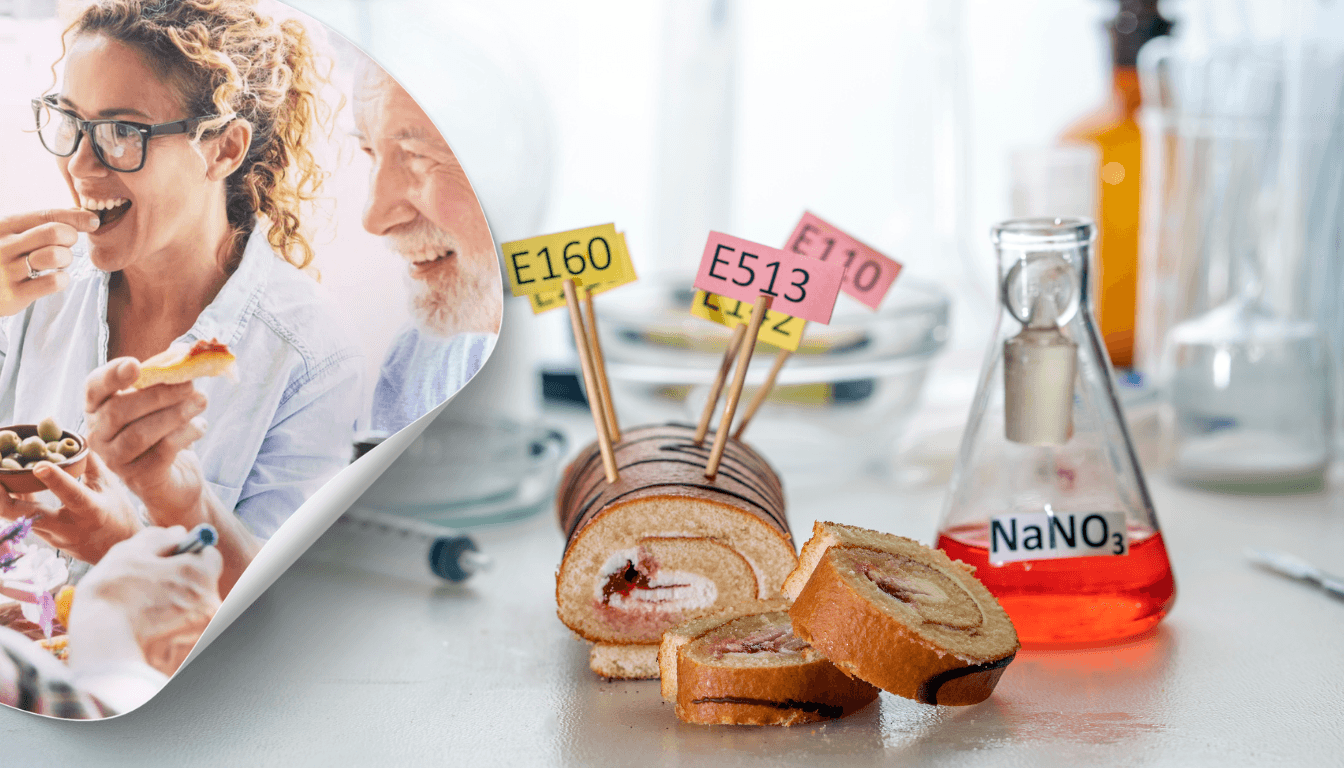
In the busy local supermarket, Push Mookim, a certified personal trainer, stops to read a pastry packet’s ingredient list. He sees names of food additives like Yellow #5 and Titanium Dioxide, legal in the US but banned in Europe. He worries about the health risks these chemicals might cause. This concern is shared by many Americans who learn about international food safety rules. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) in Europe bans harmful additives quickly. However, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the U.S. is much slower, keeping risky additives like Potassium Bromate on the shelves.
Research has long shown the risks of these additives. Red Dye 3, for example, was labeled a possible cancer-causing agent in 1990 but was only banned in America after 33 years. In Europe, such evidence leads to strict regulations. The FDA’s slow action is evident. It took over 30 years to ban Brominated Vegetable Oil, long after Europe did. California has banned certain additives, showing some states are stepping in where the federal response lags,
The U.S based, Center for Science in the Public Interest (CSPI) a non-profit is upset with the FDA’s slow response to the dangers of additives like Red Dye 3 in animals. The Environmental Working Group (EWG) another non – profit, helps consumers by listing ‘dirty dozen’ food additives to avoid, even those allowed in the US. As scrutiny increases, companies like Entenmann’s Producer of baked goods under the Hostess brand, are still using risky additives even though they have made attempts to remove some of them.
Food Additives with Known or Potential Health Risks
Some food additives approved by the FDA have been linked to health concerns, including cancer, behavioral issues, mimicking natural hormones, and hyperactivity. Below is a list of known or potential carcinogens and other harmful additives still allowed in the U.S. but restricted or banned in other countries.

Artificial Food Dyes (Red 40, Yellow 5, Yellow 6)
Commonly Found In: Candy, sodas, cereals, baked goods, and snacks.
Health Risks: Studies have linked these dyes to hyperactivity and behavior problems in children. In addition, some of these dyes contain benzidine, a known carcinogen.
Example: Red 40 has been banned in many countries like Norway and Finland, but it remains widely used in the U.S.
BHA (Butylated Hydroxyanisole) & BHT (Butylated Hydroxytoluene) Commonly Found In:
Cereals, chips, butter, and other processed foods.
Health Risks: Both BHA and BHT are linked to cancer, especially in animal studies. These additives are also considered endocrine disruptors, potentially interfering with hormone production.
Example: BHA has been banned in many European countries due to its cancer-causing potential.

Sodium Nitrite & Sodium Nitrate
Commonly Found In: Processed meats like bacon, hot dogs, and deli meats.
Health Risks: These chemicals can form nitrosamines, which are known carcinogens. Consuming large amounts of processed meats has been linked to an increased risk of colon cancer.
Example: Studies suggest that nitrate-rich foods like cured meats may raise cancer risks, especially when consumed in large quantities.
Propylparaben
Commonly Found In: Baked goods, tortillas, and other processed foods.
Health Risks: Propylparaben is known to be a hormone disruptor, particularly affecting reproductive health. It can interfere with the endocrine system and has been linked to fertility issues.
Example: Often used in products where preservatives are needed, propylparaben can also cause skin irritation in some people.

Aspartame
Commonly Found In: Frozen foods, snacks, and crackers.
TBHQ (Tertiary Butylhydroquinone)
Health Risks: TBHQ has been associated with immune system damage and neurotoxicity in high doses. Long-term exposure to this preservative can lead to serious health concerns.
Example: It is used as a synthetic antioxidant to prolong shelf life but has raised concerns for toxic build-up in the body.
Additives to Use with Caution (Moderate Health Concerns)
Monosodium Glutamate (MSG)
Commonly Found In: Fast food, soups, snack foods, and Asian cuisine.
- Health Risks: MSG is often associated with the so-called “Chinese Restaurant Syndrome”, where individuals report symptoms like headaches, sweating, and heart palpitations.
- Example: While it’s generally recognized as safe by the FDA, some people are sensitive to it, experiencing mild allergic reactions.
Xanthan Gum
Commonly Found In: Salad dressings, sauces, and gluten-free products.
- Health Risks: In large quantities, xanthan gum can cause bloating, gas, and digestive distress, especially in people with sensitive stomachs.
- Example: Individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or other digestive conditions may experience exacerbated symptoms.
Guar Gum
Commonly Found In: Ice cream, sauces, and processed foods.
- Health Risks: Like xanthan gum, guar gum can cause gas, bloating, and stomach cramps in sensitive individuals when consumed in large amounts.
- Example: Guar gum is used as a thickening agent, but its overuse can be problematic for those with digestive issues.
Polysorbates (Polysorbate 80, Polysorbate 60)
Commonly Found In: Ice cream, baked goods, and processed foods.
Commonly Found In: Cola drinks and sodas.
- Health Risks: There are concerns that polysorbates can disrupt gut bacteria and contribute to inflammation in the body, which could affect overall digestive health.
- Example: These emulsifiers are often used in low-fat or processed food to improve texture and prevent separation.
Phosphoric Acid
- Health Risks: Phosphoric acid is a tooth enamel eroder and can weaken bones when consumed in excess over time. High consumption of sodas has been linked to osteoporosis and other bone health issues.
- Example: The acidity of cola beverages can lead to a higher risk of tooth decay and bone thinning in the long term.
Sorbitol, Mannitol
Commonly Found In: Sugar-free gum, candy, and diet foods.
- Health Risks: These sugar alcohols are known to cause digestive issues like gas, bloating, and diarrhea when consumed in large amounts.
- Example: While they help reduce calories in sugar-free products, their consumption can be problematic for people with sensitive stomachs or those prone to diarrhea.
Key Takeaways
- The FDA still allows many additives banned in other countries (e.g., EU, UK, Japan).
- Minimizing processed foods can help reduce exposure to potentially harmful additives.
- Advocacy groups continue pushing for stricter regulations in the U.S.
- Foods additives banned in Europe but legal in the USA continue to raise health concerns.
- Reports from the FDA acknowledged the potential harms of additives such as Red Dye 3, yet a ban was only implemented 23 years after the danger was recognized
- International food regulations encourage consumers to remain vigilant about the ingredients in their purchases
- The gap in food safety standards between the EU and USA illustrates a significant discrepancy in public health policy
- State legislation, such as California’s, underscores the urgency surrounding the removal of harmful additives from foods
- Consumer advocacy groups and EWG resources play a critical role in education about food safety
- Market response to organic foods and less-processed food highlights a shift toward health-conscious eating
- The US and EU hold sharply different stances on food additives, with many banned in Europe permitted in America.
- Knowledge about these differing regulations is key to making informed dietary choices.
- Critical health risks such as carcinogenic potential are at the heart of European bans concerning substances like potassium bromate.
- Consumer advocacy and state-led regulations in the US, such as California’s ban on certain food dyes, indicate increasing concern over food additive safety.
- Evaluating food labels with a keen eye for these additives can help consumers avoid potential risks.
The Role of Food Additives in the Food Industry
In the USA, over 10,000 chemical substances are used as food additives. Interestingly, nearly all of these were added to the list after 2000 and most approvals came not from the FDA, but from the food and chemical industries themselves, which is ridiculous at best. Because of an obvious pandering to self interest, concerns have been raised about the long-term health effects of these additives

Discover Your Body’s Unique Needs – No Blood, No Needles, No Hassle!”
With just 10 strands of hair, you can test for 750+ food sensitivities and intolerances, plus gain insights into your appetite hormones, anti-aging compounds, internal inflammation, sleep hormones, and stress levels.
- Don’t Wait – Your Health Can’t Wait!
- 👉 [Order Now] and take the first step toward understanding your body like never before.
Overview of Regulations in Europe and the USA
In comparing EU food laws with FDA guidelines, big differences are clear. European rules demand full safety checks before additives can be used. In the US, some additives haven’t been rechecked since 1969. This shows a big difference in how each approaches food additive safety.
The European Union’s rules are all about protecting consumers and stopping health before they arise. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) plays a key role in keeping these standards high. They do this by strictly regulating food additives and ingredients.
EFSA: The European Food Safety Authority
The EFSA checks all food additives and other possible biological and heavy metal contaminants before deciding whether foods are safe for the European market and works to make sure that safety standards are the same in all 27 EU countries.
The FDA’s job is to keep the public healthy by checking on food, medicine, and more. It uses a system called Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS). This lets manufacturers decide if an additive is safe without the FDA’s ok first. Because of this, almost all new chemicals added to food since 2000 were called safe by the companies that made them
Europe also requires more allergens to be listed on food packaging than the US does. This careful action highlights Europe’s attention to detail in handling food safety concerns
Food Additives: Classification, Benefits, and Risks
The Process of Approving Food Additives
Adding new food ingredients in the EU involves a lot of checks. Each one must go through tough safety tests. This includes checking for any negative effects on health. This careful process makes sure that all additives in the European market are very safe.
Unlike in the US, where additives are often seen as safe until proven otherwise, the EU prefers to prevent problems before they happen. This careful approach does two main things. It keeps consumers safe. And, it makes people around the world trust that European food is very high in quality and safety.
Understanding Food Safety Regulations in the USA (Definitions)
- Incidental Additives – Additives that are present in trace amounts and do not serve a technical function in the final product (e.g., processing aids, carryover ingredients) may not need to be listed.
- GRAS Substances – Ingredients that are “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS) may not be considered food additives and might not always be separately listed.
- Collective Terms – Some additives may be grouped under generic terms, such as “spices,” “natural flavors,” or “artificial flavors,” rather than being named individually.
Differences in Acceptable Levels of Products
The U.S. and EU see food safety differently because of their different rules. The U.S. doesn’t use E-number labels. So, people might not know what’s in their food The U.S. usually lets new additives be used unless they’re shown to be bad. This way of thinking relies a lot on the GRAS system. With GRAS, companies check the safety of substances, not the FDA
These differences highlight why strong FDA rules and clear food labels are key for safety. Knowing these differences helps people make better choices in the complex world food market.
Notable Food Additives Banned in Europe
Potassium Bromate: A Common Baking Ingredient
Potassium Bromate was once a favorite in baking for making dough better. But, it’s not allowed in the European Union because it might cause cancer. Studies show it causes tumors in animals.
Azodicarbonamide: The Dough Conditioner
Azodicarbonamide (ADA) helps make baked goods’ texture and color better. But, Europe banned it in 2005. This is because when heated, ADA turns into a cancer-causing chemical.
Butylated Hydroxyanisole (BHA): A Preservative
BHA helps keep food fresh and maintains its color, but Europe limits its use. Some groups say it might cause cancer, and California even lists it as a carcinogen. It’s also linked to causing tumors in animals and messing with thyroid hormones
The European Union’s hard stance on these additives shows its dedication to high food safety. In contrast, the U.S.’s methods, which rely on reviews after a product is sold, show a big difference. Here, Europe’s action shows how serious it is about keeping food safe
This examination of banned food additives reveals the different safety precautions around the world. It also highlights how Europe takes strong steps to protect its people’s health through tough food laws.
Food Additives Approved in the USA
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is key in controlling food additives in the United States. It ensures public safety and health. But, the OK of some additives has caused big arguments. This happens especially when these are banned or limited in places like the European Union.
The Controversy Surrounding These Additives
There’s a big difference between how the FDA and other global regulators view the safety of food additives. For example, the FDA once allowed substances like Potassium Bromate and Brominated Vegetable Oil (BVO). But now, there’s a change in how they’re seen due to new insights and public health efforts. Potassium bromate is cancer-causing but still legal in the U.S., while Europe has banned it. BVO was okayed in 1977 by the FDA but is now banned in the EU3. This highlights serious worries about the health dangers of some additives still allowed in the USA.
Health Risks Associated with Approved Additives
Groups like the Environmental Working Group (EWG) and the Center for Science in the Public Interest (CSPI) spotlight dangers from specific FDA-regulated additives. They point out issues with substances like Propylparaben, BHA, and BHT. These are thought to mess with fertility, hormones, and might even cause cancer. Despite their concerns, the U.S. allows over 10,000 chemicals in food. Many of these haven’t been checked by the FDA, but by the food industry itself Even synthetic ingredients in organic foods must be reviewed every five years. This shows a vital, ongoing process for checking food safety
To wrap up, FDA’s efforts aim at making sure food additives are safe. However, the ongoing debates and new research point out the importance of keeping an eye on the health risks. These concerns involve additives still in American foods.
Color Additives: A Case Study
The debate over food coloring agents, especially those banned, is a big health and safety concern. It’s crucial to understand these additives and their regulations to help health-aware people.
Tartrazine: Yellow
Tartrazine, or Yellow 5, shows how food safety views differ between the U.S. and Europe. It’s known for possible health risks like allergies.
In Europe, there are strict rules for labeling Tartrazine, and some places even ban its use in food due to health worries. Meanwhile, the U.S. FDA still approves its use, showing a big difference in food safety standards.
Red Dye 3, found in some foods and products, is banned in various states. It joins Potassium Bromate and Brominated Vegetable Oil (BVO) in a list of debated additives. BVO was banned just recently in 2023. This shows the ongoing struggle and complex rules around food safety in the U.S.
| Additive | Status in EU | Status in USA |
|---|---|---|
| Tartrazine (Yellow 5) | Restricted/Banned | Allowed |
| Red Dye 3 | Banned in many areas | In January 2025, the FDA prohibited the use of erythrosine (Red Dye No. 3) in all foods and ingested drugs, citing evidence of carcinogenicity at high doses |
| Potassium Bromate | Banned | Allowed |
| Brominated Vegetable Oil | Banned | Recently banned (2023) |
California has been a leader in tightening food safety rules in the U.S. in 2023 , it banned brominated vegetable oil, potassium bromate, propylparaben, and Red Dye No. 3, This act, and others like it, show a move towards safer food. Unfortunately these bans in the USA are not enforceable until 2027.
Still, having the conversation and laws changing around banned additives and food colors is very important. They lead to better safety for consumers, making people more aware and cautious about what they eat.
Understanding food additives is key to a healthy diet. This topic gets complicated when comparing American and European rules. In the U.S., many foods have additives like potassium bromate, found in over 130 breads and doughs. These additives, often banned in Europe for health reasons, spark big debates on food safety
In Europe, almost all these chemicals are banned, showing a clear difference in food safety views. Meanwhile, in America, these additives are common in our kitchens. For example, while the U.S. uses potassium bromate, raising health concerns, Europe avoids it because it might cause cancer. This big difference in food laws highlights the importance of understanding what’s in our food.
Food Preservatives Good or Bad
Let’s now focus on Sodium Nitrite and Propyl Gallate. They have caused health worries worldwide. We will look at how the USA and Europe handle these substances.
Sodium Nitrite: A Cancer Risk
Sodium Nitrite keeps processed meats looking good and safe from bacteria. But, this preservative could increase cancer risk, causing concern. Europe has set strict rules on how much can be used. This shows they’re serious about keeping people safe.
Propyl Gallate: A Possible Carcinogen
Propyl Gallate is in many edible items but might disrupt hormones. Studies suggest it could even harm human fertility This raises questions about its safety in foods. It’s clear we need to take a closer look at it.
Scientific and medical studies keep finding problems with certain food additives. As a result, some are getting banned. This happens when new evidence of their harm comes to light.
| Preservative | Status in USA | Status in EU |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium Nitrite | Limited use under FDA regulations | Tightly regulated with stricter limits |
| Propyl Gallate | Allowed with safety evaluations | Subject to review and potential bans |
We’re always rechecking the safety of food preservatives like Sodium Nitrite and Propyl Gallate. People want food that’s safe and transparent. This pushes us to think again about what’s okay to eat.
Artificial Sweeteners: The Divide
Many people are worried about artificial sweeteners, with some places even banning them. A big debate revolves around two sweeteners: aspartame and sucralose. They show how differently the United States and the European Union handle these substances.
Aspartame: Risks and Regulations
The story of aspartame getting approved for use in food sheds light on differences in food safety standards around the world. The U.S. FDA first said yes to aspartame in 1974 after looking at 168 studies. But they had to pause in 1975 to check the quality of those studies. Despite doubts, aspartame stayed approved for use. Both the FDA and the European Food Safety Authority say it’s safe to eat if you don’t have too much.
But aspartame’s journey wasn’t smooth. In 1996, a report showed some FDA officials doubted its safety. The internet also spread scary stories about it. This made aspartame one of the most talked-about sweeteners.
Sucralose: Banned or Approved?
Sucralose has been closely looked at too. It’s okayed in over ninety countries because it can handle heat well. This makes it good for cooking and baking. Yet, the way different countries see sucralose and similar sweeteners varies a lot.
When we talk about banned food additives, it’s interesting to see such different decisions. For example, the U.S. banned cyclamate in 1969 because it might cause cancer. But the European Union still allows it in certain cases
How people view aspartame and sucralose’s safety shows a bigger talk about banned food additives. It highlights big differences in health policies and safety checks between regions.
| Sweetener | Status in the USA | Status in the EU |
|---|---|---|
| Aspartame | Approved | Approved with Regulation |
| Sucralose | Approved | Approved under Controlled Conditions |
| Cyclamate | Banned | Approved under Controlled Conditions |
This difference in rules about artificial sweeteners points to the challenge of managing food safety worldwide. It shows we need ongoing research and rules that can change with new science and health needs.
Consumer Awareness and Labeling
Understanding food labels is key in today’s worldwide market. This helps promote safety and awareness. Different places, like the European Union and the United States, have their own rules. So, consumers play a big role in avoiding health risks from food additives.
Importance of Reading Food Labels
Food labels are your first shield against harmful ingredients. The EU limits many more ingredients than the U.S. This shows the big differences in what’s considered safe. By learning about these variations, people can steer clear of additives that are okay in the U.S. but banned elsewhere. This includes some parabens and phthalates20.

“Take Control of What’s on Your Plate – Protect Your Health Today!”
Learn what’s in the food you eat every day? Is the food you eat sabotaging your health.
In this book
- Identify and eliminate the 13 most dangerous ingredients lurking in your food.
- Learn how artificial colors and preservatives are linked to ADHD in children.
- Discover the hidden industrial waste products and toxic metals in your meals.
- Uncover the truth about synthetic sweeteners and their impact on your health.
Knowledge is power – and your health is worth fighting for!
👉 [Get Your Copy Now] and start making informed choices for you and your family
Resources for Safe Eating
How to Identify Banned Food Additives
Thanks to tech, apps can check product barcodes for ingredient info. They highlight ingredients that are not allowed in certain places. For example, titanium dioxide is okay in the U.S. but not in France or the EU because it might be risky.
The Environmental Working Group (EWG) offers databases to help find safer foods. It shows how important such groups are in making the public aware and pushing for better food safety laws. Their work is crucial because there’s a big gap in how food chemicals are checked for safety. Many substances haven’t been thoroughly evaluated in a long time
| Restricted/Banned Additive | Status in EU | Status in U.S. |
|---|---|---|
| Parabens | Banned/restricted | Widely used |
| Phthalates | Restricted | Legal in many products |
| Titanium Dioxide | Banned | Widely used in food products |
| Brominated Vegetable Oil | Varies | Banned in California |
Taking Action: What You Can Do
There’s never been a more vital time to push for stronger food safety standards. Every buying decision we make can improve health and guide the industry’s direction. Here’s how you can help improve standards and make healthier choices.
Advocacy for Food Safety Reform
Raising your voice for food safety can really make a difference. By getting involved in policymaking, like commenting on FDA proposals you help shape better rules. Advocacy ensures our needs are considered and pushes for tighter limits on unsafe additives. Taking a stand for laws that ban harmful chemicals, like the cancer-causing potassium bromate – still used in the U.S. but banned in Europe can vastly improve our health.
Choosing Organic and Natural Products
Going organic is a smart move to avoid risky chemicals. Organic standards in the U.S. ban harmful pesticides and fertilizers, protecting bees and preventing water pollution Plus, buying organic supports more sustainable farming, which is better for the planet.
In the end, both FDA rules and food safety standards are key to keeping us safe, but we also have a big role. By pushing for better laws and picking organic, we help build a healthier food system. Our individual efforts, combined with group action, can really improve food safety rules.
Conclusion: Making Informed Food Choices
Understanding global food rules is key to promoting food safety and health. The difference in food additive policies between Europe and America shows varying approaches to safety and public health demands. Europe tends to be ahead, banning harmful additives like titanium dioxide for safety.
Meanwhile, the United States leans toward allowing more processed foods, which correlates with higher obesity rates28.
Summary of Key Differences
The global difference in food laws highlights why making smart food choices is crucial. It’s up to consumers to navigate these rules for their health. For instance, the EU has banned additives like Artificial colors and Olestra unlike the FDA, which permits them.
This gap underlines the importance of being informed and careful with our food decisions.
Final Thoughts on Food Safety and Health
Making smart food choices gets easier with knowledge of rules and why they exist. Bodies like the EFSA and FDA shape the food world and influence our views on what’s safe. Changes in rules can create barriers, and safety opinions differ.
Consumers need to use resources, get involved in discussions for global rule alignment. By reading labels, looking at evidence, and advocating, we help improve food safety and promote health awareness.
FAQ
What are food additives?
Food additives are substances we add to food. They help keep it safe, fresh, tasty, and looking good. These include things like preservatives, flavor enhancers, colorings, and sweeteners.
How do food safety regulations differ between Europe and the USA?
In Europe, the EFSA makes sure food additives are safe before they’re used. They follow a rule that says “better safe than sorry.” But in the USA, the FDA lets additives be used until they’re shown to be harmful. This means something might be used in food for a longer time in the USA before it’s considered unsafe.
What is the role of the EFSA?
The EFSA’s job is to check on risks that food might have. They give advice based on science about these risks. This helps make sure that food additives are safe in the European Union.
Can you give examples of additives banned in Europe but legal in the USA?
Sure, Potassium Bromate and Azodicarbonamide, used in making bread, are banned in Europe. So are some dyes like Tartrazine (Yellow 5). They’re banned in Europe because they might not be safe, but are still used in the USA.
What is the FDA’s role in food safety in the USA?
The FDA works to keep us healthy by making sure food, drugs, and other products are safe. This includes checking on everything from medicine and makeup to food and devices that could emit radiation. They also look at tobacco products.
Why are some additives controversial?
Some additives are debated because they could be harmful, like causing cancer or messing with our hormones. The FDA might not ban these right away, and that can make people worried.
How important is it to read food labels?
Reading food labels is super important. They tell us what’s in our food, including the additives. This info helps us choose healthier options and avoid stuff that might not be good for us.
What are some resources for consumers to learn about safe eating?
For safe eating tips, check out the Center for Science in the Public Interest, the Environmental Working Group, and the EFSA. They offer lots of info on what food additives to stay away from.
What actions can consumers take to advocate for food safety reform?
To help change food safety laws, learn about additives and share that knowledge. Choosing organic and natural products can also make a difference. Supporting laws for better food safety and sharing your concerns with the FDA can help too.
Why might someone choose organic products in relation to food additives?
Organic foods don’t have many synthetic additives or pesticides, and they avoid GMOs. Choosing organic can lower your exposure to some controversial additives found in regular foods.





